An undervalued stock represents that the market consensus view of that company is negative. If every market participant sees the outlook for a company to be negative, this will be reflected in the stock valuation. This is the key reason that explains why some stocks are undervalued.
Is it good if a stock is undervalued?
It is good to consider buying an undervalued stock, that is what some of the most successful investors have consistently done over time. However, not every undervalued stock is worth considering. There are value traps among those undervalued stocks, and investors need to be able to pick the right ones. Thus, it is also important to know how to identify value traps.
What happens if a stock is undervalued?
An undervalued stock implies that the market is not valuing the business correctly. Therefore its valuation and stock price do not represent the accurate value of the business behind the stock.
An undervalued stock is a stock with a low valuation, that represents the negative perception of the market towards that business. This means that both retail investors and institutional investors think the business will continue to perform poorly.
Is it better to buy undervalued or overvalued stocks?
Broadly speaking it is better to buy an undervalued stock than an overvalued stock. This is because the undervalued stock is expected to go up in price, and the overvalued stock is expected to drop.
When addressing this issue it is important to understand that stock valuation is a mix between art and science. It is nearly impossible to accurately value a business, as there will always be discrepancies between the true value, and the valuation attributed based on expectations.
What valuations can a stock have?
In terms of valuation a stock can be considered:
- Undervalued
- Fairly valued
- Overvalued
Undervalued stocks are often related to value stocks, and value investing. Conversely, overvalued stocks tend to be associated with growth investing.
Value stocks have proven to have a better performance over the long term. However, this does not mean that overvalued stocks might not continue to go up in price during a short period of time.
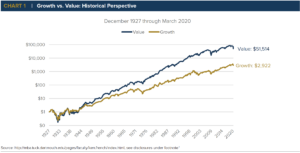
Source: Anchor
Is it bad to buy an overvalued stock?
It is bad to buy an overvalued stock, instead, investors should short the stock if it is overvalued. The stock market is unpredictable, and an overvalued stock might continue to increase in price for a long time.
Therefore, investors should be aware that even if a stock is overvalued, it might take a considerable amount of time before it finally drops to a fair valuation or slight overvaluation.
How do you pick a stock that is undervalued?
Picking undervalued stocks is what is commonly referred to as value investing, and it is based on fundamental analysis. This means researching and analyzing the business in order to determine its valuation. If you are able to value the business correctly, the market will eventually agree with you.
In order to do so, you need to have more information on the business than your competitors, which are all of the other investors analyzing the same stock. Be aware that your insights into the business or the industry are extremely important. This is why legendary investors like Warren Buffett and Charlie Munger advocate that you should stick to your circle of competence, and continuously expand it.
Investors should be aware that the gap between their valuation of the business, even if it is correct can take years to be reflected on the stock price. This is one of the reasons investors give up their strategy and approach to picking undervalued stocks.
Although some investors have continuously advocated that value investing is dead, that is not true. In order to pick stocks that are undervalued, you need to research the business and be familiar with different types of valuation approaches.
How buying undervalued stocks works
Whenever a trade is made there are two opposing views. The investor buying is bullish and the investor on the other end of the trade (selling) is bearish. When you buy a security, you are essentially taking an opposing view to the broader market.
Essentially you are attributing a higher value to the business than the market, and you generate a profit when there is a rerating.

