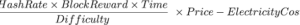Bitcoin has been the hottest investment in the last few years. Touted by many as the new digital gold, crowds of crypto fanatics have been driving its price higher. But what are the differences between Bitcoin vs Visa? Which one of these payment systems is more efficient?
In this overview, we will analyze some of the risks associated with Bitcoin, and the possible implications of Bitcoin mining. We will also compare Bitcoin vs Visa, to see if Bitcoin could ever become a major payment system.
The invention of cryptocurrencies
There is no doubt that the invention of cryptocurrencies has been a great achievement. No longer are we dependent on currencies issued by Central Banks. Decentralized currencies have many advantages but also a few critical disadvantages.
It allows holders to transact without being tracked. And this is the main reason Bitcoin is the preferred payment method of dark web users and it is known as the main currency used by people involved in illegal activities.
What are the disadvantages of a decentralized cryptocurrency?
Being a decentralized currency prevents third-party seizures (wealth confiscation) and taxes from being charged on both transactions. As Bitcoin approaches a new all-time high, it is important to keep in mind its limitations.
On one hand, the fact that Bitcoin is a completely computerized currency, allows highly skillful hackers to easily steal it.
The fact that it is untrackable is a double-edged sword. As we have seen in 2018, $1.1 billion worth of cryptocurrency was easily stolen, and recently the Feds have seized $1 billion in stolen Bitcoin from Silk Road, once the biggest marketplace on the dark web.
How bitcoin mining works
Since Bitcoin is a decentralized currency, it relies heavily on Bitcoin miners. These 21st-century miners do not use pickaxes or canaries to warn them when to run. They mine virtual gold that is incredibly scarce and highly valued.
They rely on powerful hardware connected in order to process transactions. As transactions are processed miners unlock new Bitcoin blocks.
There are only 21 million Bitcoins available. In the first 10 years since the launch of Bitcoin 18.5 million coins have been minted. That leaves roughly 2.5 million Bitcoins to be mined until 2140. Based on Zeno’s paradoxes, the output of Bitcoins mined is reduced every 4 years.
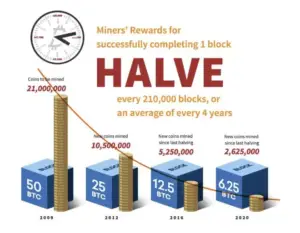 Source: Investopedia
Source: Investopedia
So far Bitcoin mining has been an incredibly profitable activity. But there is no guarantee that it will continue.
What influences the profitability of Bitcoin miners?
Bitcoin miners rely on different variables that make their operations profitable. There are 3 main variables that influence the profits and sustainability of Bitcoin, and the blockchain network:
- The price of the Bitcoin they mine
- Their electricity cost to process the transactions
- Hardware efficiency
Given that Bitcoin has been trading around all-time highs, even with the reduction this year in mining blocks. The increase in price has made up for that. Instead, miners focus most of their attention on energy costs and hardware efficiency, because those are the two variables that they can control.
Choosing the right hardware is one of the most important steps in setting up your Bitcoin mine.
How Difficulty Affects Bitcoin Miners
Choosing the right hardware can provide long-term efficiency, and increase mining profits. Bitcoin miners relentlessly study the efficiency of different GPUs and CPUs. With a keen focus on power consumption and hash rate.
The speed at which a computer can complete an operation in Bitcoin code is commonly designated as the hash rate. Another variable to keep in mind is the difficulty. Since Bitcoin blocks are assigned to miners randomly. The difficulty defines the average time between blocks of crypto.
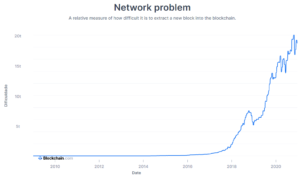 Source: Blockchain
Source: Blockchain
The difficulty has been increasing exponentially, due to the reduction of blocks available to mine. Businesses with high operating margins are usually bound to face a lot of competition.
As competitors realize the profit margins and decide to take a shot at it themselves. The same has been true for crypto mining. Not only have blocks diminished, but the higher competition has made it increasingly difficult to mine a single block.
How are Bitcoin miners' profits calculated?
The following simplified formula is the easiest way to calculate the expected profit of cryptocurrency miners:
Source: Honeyminer
The hash rate determines the processing power of the network. In essence, it is the speed at which miners can solve the puzzles. It differentiates efficient and inefficient miners, and it is mainly driven by GPU, software, and overclocking.
Overclocking is simply a way to set up your hardware so it can perform as efficiently as possible.
Bitcoin Mining Risks
Although Bitcoin mining has been a rising industry with a lot of interesting companies stepping into the space, there are several risks that miners face.
Here are a few risks and factors miners and bitcoin buyers relying on the network need to consider:
Mining competitiveness
The increased competitiveness can hinder the profitability of most miners, as the number of blocks available to mine will eventually decrease even more in 2024. This in turn could pose a threat to the blockchain system. If the competition is too fierce, miners may not be able to mine the amount of Bitcoin needed to generate a profit or even break even.
What happens to Bitcoin Miners if the price of Bitcoin goes down?
Another factor to keep in mind is the price of Bitcoin. If Bitcoin prices decline to a certain threshold, mining may become an unprofitable activity. Given that the competition has increased tremendously over the years, Bitcoin miners see their margins shrink day by day. The only thing supporting and increasing their margins is the price at which Bitcoin trades.
What happens to Bitcoin after 2140?
Another important question that nobody seems to be able to answer is what happens to Bitcoin after 2140. In 2140 the last Bitcoin will be mined. When that happens independently of the price of Bitcoin, what will be the incentive for miners to keep on processing transactions?
Nobody seems to be able to understand the risk that this poses to the whole system. One of Bitcoin’s advantages is the fact that the miners are processing all of these transactions to receive fractions of Bitcoins. This happens because miners are able to mine Bitcoin as they process transactions.
After 2140, miners will only receive a transaction fee. What will happen to Bitcoin miners when their main incentive does not exist anymore? Who wants to hold a cryptocurrency that you cannot transact with?
Bitcoin fanatics usually use the argument that Bitcoin has value because it has a finite supply of 21 million. But in reality, they never dig deep enough to realize that unless the supply increases, miners will not be incentivized to process their transactions.
Bitcoin vs Visa
In order to understand exactly how Bitcoin’s future as a payment system could ever be considered a possibility, we need to compare several important aspects of Bitcoin vs Visa.
Visa remains the preferred payment system used worldwide and there is a reason for that.
Bitcoin vs Visa: Transactions
Another aspect that is usually overlooked is the fact that Bitcoin transactions are extremely inefficient. Bitcoin processes a fairly small number of transactions. Particularly when compared with regular electronic transactions processed by financial service companies, the likes of Visa (NYSE: V) and Mastercard (NYSE: MA).
What is the size of the cashless transaction market worldwide?
Cashless transactions worldwide are estimated at around 708.5 billion transactions per year. They are also expected to grow to over one trillion in 2023.
Source: World payment report
How many transactions does Bitcoin process daily and yearly?
Bitcoin has an average of 300,000 transactions daily or 109.500 million transactions yearly. That represents only 0.022% of all of the transactions processed worldwide. For comparison, Visa processes 150 million transactions on a daily basis. Every day around the world there are roughly one billion credit card transactions.
Why Bitcoin can never be used as a global payment system
Blockchain seems to have a scalability problem. For the number of transactions to increase drastically, it is required that the number of miners grows exponentially. This is one of Bitcoin's biggest risks.
Source: Blockchain
If there are too many miners processing Bitcoin transactions, the fierce competition will increase the difficulty. Increased difficulty for miners will translate into lower margins.
As more miners try to chase the same amount of reward blocks, not all of them will turn a profit. This is a threat to the whole Blockchain network and the main reason why Bitcoin could never be used as a global payment system.
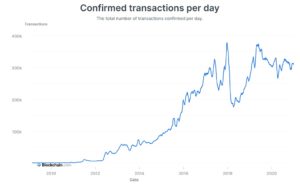
Is Bitcoin used for transactions?
The data shows that Bitcoin might only be used for speculation, because of the correlation between Bitcoin’s price and the number of transactions. When Bitcoin prices are higher, the number of transactions also seems to follow along.
Source: Blockchain
Bitcoin vs Visa: Energy Consumption
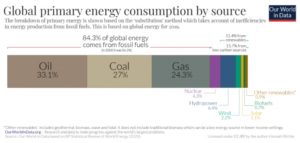
Global electricity consumption is expected to grow faster than the population. China is already the country with the largest consumption of electricity, with 6,011 TWh consumed in 2018. It is followed by the US, India, Japan, and Russia, with 3,901 TWh, 1201 TWh, 946 TWh, and 760 TWh respectively.
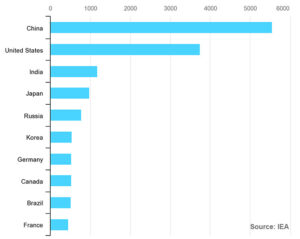
Source: IEA
How much electricity does Bitcoin consume?
Bitcoin’s electricity consumption is so high that it equals that of Switzerland. At 58.93 TWh per year, it represented 0.21% of the energy consumed worldwide in 2019. At the same time, Bitcoin transactions represent 0.015% of all cashless transactions worldwide. Some estimates point to even larger numbers. Comparing Bitcoin’s energy consumption with countries like Chile.
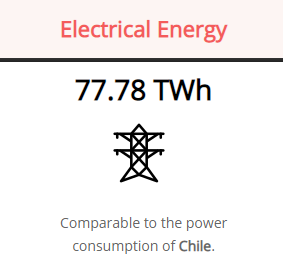 Source: Digiconomist
Source: Digiconomist
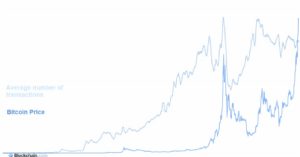
What percentage of the global energy consumption do Bitcoin transactions represent?
Given that global consumption of energy is around 173,340 TWh. Bitcoin transactions represent 0.45% of all the energy consumed worldwide.
Source: Ourworldindata
Digiconomist goes even further stating that a single transaction of bitcoin, is the equivalent of the power consumption of an average US household during 23.55 days.
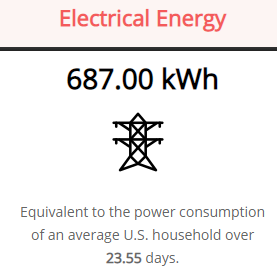 Source: Digiconomist
Source: Digiconomist
How much energy is needed for Bitcoin to process the same amount of transactions as Visa?
If Bitcoin were to process Visa’s 54.75 billion transactions yearly. It would require 38,854 TWh. Or essentially 22.4% of all of the energy consumed worldwide.
How much energy is needed for Bitcoin to process all cashless transactions?
To power all of the 700 billion cashless transactions happening worldwide yearly using Bitcoin. It would require 480,900 TWh, nothing more than a 177% increase in the energy consumed worldwide in 2019.
Bitcoin advocates usually argue that it is the solution to all of mankind's financial problems. They assume Bitcoin would be able to process most of the transactions worldwide if not all.
If that was the case we would need to produce 177% more energy than what we do now. The energy inefficiency of Bitcoin transactions is its main Aquiles heel.
Bitcoin vs Visa: Carbon Footprint
We will also need to compare the carbon footprint of Bitcoin vs Visa, to understand the environmental implications of using Bitcoin. In 2019 roughly 43.1 billion tons of CO2 were emitted into the atmosphere.
What is the carbon footprint of Bitcoin?
According to Joule, Bitcoin was responsible for 5.1% of the CO2 emissions in 2019. Using the estimated amount of CO2 Bitcoin produces annually according to Digiconomist - 36.95 MtCO2
 Source: Digiconomist
Source: Digiconomist
Bitcoin's carbon footprint if it processed all of Visa’s transactions
If Bitcoin were to process the same amount of transactions as Visa - 150 million daily transactions. Taking into account Bitcoin’s 300,000 daily transactions it would generate roughly 18,475 Mt CO2 yearly. That would represent nearly 43% of all the CO2 emissions in 2019 around the world. According to Digiconomist, the carbon footprint of a single Bitcoin transaction is the equivalent of 717,673 Visa transactions.
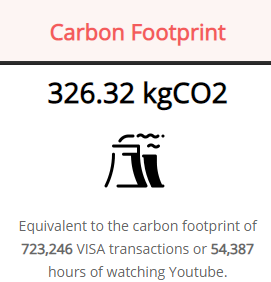 Source: Digiconomist
Source: Digiconomist
What would be Bitcoin’s carbon footprint if it processed all the cashless transactions in the world?
Let’s say hypothetically, that Bitcoin would process all of the 700 billion transactions that are done worldwide in a year. That would result in a whopping 236,210 Mt CO2 emissions. An increase of nearly 450% compared with our emissions in 2019, of 43.1 billion tons of CO2. In essence, Bitcoin can be extremely detrimental to our environment.
As bitcoin transactions increase so will its carbon footprint. Since over 84% of the energy consumption worldwide comes from fossil fuels. Bitcoin’s increasing energy needs will continue to damage our environment.
Source: Ourworldindata
Bitcoin vs Visa: Electronic Waste
Another consequence of the blockchain system is the amount of e-waste it produces. Given the fact, that is highly dependent on state-of-the-art hardware, the mines can run at the highest capacity possible.
Source: Digiconomist
Bitcoin transactions end up creating a lot of e-waste related to hardware that is no longer efficient or desirable.
Bitcoin vs Visa: The Verdict
Bitcoin’s lack of efficiency when it comes to processing transactions is clearly one of the biggest risks it faces. The blockchain is both energy inefficient and environmentally unfriendly. The increased energy we would have to produce to process most of the transactions worldwide with Bitcoin is simply not feasible.
While at the same time, the blockchain system does not seem to ever be able to process transactions at a certain speed. Bitcoin is clearly not an investment vehicle nor is it a store of value as some tout, but you can buy bitcoin cash.
It is merely a sophisticated way of conducting transactions anonymously and in a decentralized way. Given its characteristics, it is favored by individuals engaged in illicit activities. As it protects them from exposure and conveys safety to transactions.
We have no position in Bitcoin. Read our disclosure.